| 16-tól kevesebb mint 17-ig | 32,50 | ||
| 17-től kevesebb mint 18-ig | 33,75 | ||
| 18-tól kevesebb mint 19-ig | 35,00 | ||
| 19-től kevesebb mint 20-ig | 36,25 | ||
| A szóló jármű, nyerges jármű vagy minden más járműkombináció két szélső tengelyének távolsága lábban | A szóló jármű, nyerges jármű vagy minden más járműkombináció megengedett legnagyobb összsúlya fontban | ||
| 3-tól kevesebb mint 7-ig | 32,00 | ||
| 7-től kevesebb mint 8-ig | 32,480 | ||
| 8-tól kevesebb mint 9-ig | 33,320 | ||
| 9-től kevesebb mint 10-ig | 34,160 | ||
| 10-től kevesebb mint 11-ig | 35,000 | ||
| 11-től kevesebb mint 12-ig | 35,840 | ||
| 12-től kevesebb mint 13-ig | 36,680 | ||
| 13-tól kevesebb mint 14-ig | 37,520 | ||
| 14-től kevesebb mint 15-ig | 38,360 | ||
| 15-től kevesebb mint 16-ig | 39,200 | ||
| 16-tól kevesebb mint 17-ig | 40,040 | ||
| 17-től kevesebb mint 18-ig | 40,880 | ||
| 18-tól kevesebb mint 19-ig | 41,720 | ||
| 19-től kevesebb mint 20-ig | 42,560 | ||
| 20-tól kevesebb mint 21-ig | 43,400 | ||
| 21-től kevesebb mint 22-ig | 44,240 | ||
| 22-től kevesebb mint 23-ig | 45,080 | ||
| 23-tól kevesebb mint 24-ig | 45,920 | ||
| 24-től kevesebb mint 25-ig | 46,760 | ||
| 25-től kevesebb mint 26-ig | 47,600 | ||
| 26-tól kevesebb mint 27-ig | 48,440 | ||
| 27-től kevesebb mint 28-ig | 49,280 | ||
| 28-tól kevesebb mint 29-ig | 50,120 | ||
| 29-től kevesebb mint 30-ig | 50,960 | ||
| 30-tól kevesebb mint 31-ig | 51,800 | ||
| 31-től kevesebb mint 32-ig | 52,640 | ||
| 32-től kevesebb mint 33-ig | 53,480 | ||
| 33-tól kevesebb mint 34-ig | 54,320 | ||
| 34-től kevesebb mint 35-ig | 55,160 | ||
| 35-től kevesebb mint 36-ig | 56,000 | ||
| 36-tól kevesebb mint 37-ig | 56,840 | ||
| 37-től kevesebb mint 38-ig | 57,680 | ||
| 38-tól kevesebb mint 39-ig | 58,520 | ||
| 39-től kevesebb mint 40-ig | 59,360 | ||
| 40-től kevesebb mint 41-ig | 60,200 | ||
| 41-től kevesebb mint 42-ig | 61,040 | ||
| 42-től kevesebb mint 43-ig | 61,880 | ||
| 43-tól kevesebb mint 44-ig | 62,720 | ||
| 44-től kevesebb mint 45-ig | 63,560 | ||
| 45-től kevesebb mint 46-ig | 64,400 | ||
| 46-tól kevesebb mint 47-ig | 65,240 | ||
| 47-től kevesebb mint 48-ig | 66,080 | ||
| 48-tól kevesebb mint 49-ig | 66,920 | ||
| 49-től kevesebb mint 50-ig | 67,760 | ||
| 50-től kevesebb mint 51-ig | 68,600 | ||
| 51-től kevesebb mint 52-ig | 69,440 | ||
| 52-től kevesebb mint 53-ig | 70,280 | ||
| 53-tól kevesebb mint 54-ig | 71,120 | ||
| 54-től kevesebb mint 55-ig | 71,960 | ||
| 55-től kevesebb mint 56-ig | 72,800 | ||
| 56-tól kevesebb mint 57-ig | 73,640 | ||
| 57-től kevesebb mint 58-ig | 74,480 | ||
| 58-tól kevesebb mint 59-ig | 75,320 | ||
| 59-től kevesebb mint 60-ig | 76,160 | ||
| 60-tól kevesebb mint 61-ig | 77,000 | ||
| 61-től kevesebb mint 62-ig | 77,840 | ||
| 62-től kevesebb mint 63-ig | 78,680 | ||
| 63-tól kevesebb mint 64-ig | 79,520 | ||
| 64-től kevesebb mint 65-ig | 80,360 | ||
| iv) | Ha a nemzetközi forgalomban részt vevő járművek megengedett legnagyobb összsúlya tekintetében eltérés mutatkoznék aszerint, hogy ezeket az iii) alpont táblázatában méteregységben, vagy lábban és fontban fejezték ki, a táblázat azon részének számait kell alkalmazni, amely a magasabb megengedett legnagyobb összsúlyt engedélyezi. | ||
3. A Szerződő Államok körzeti megállapodásokat köthetnek, amelyekben magasabb, megengedett legnagyobb összsúlyokat rögzíthetnek le, mint a jegyzék számértékei. Mégis ajánlatos, hogy a legjobban terhelt tengelyre megengedett legnagyobb súly ne haladja meg a 13 tonnát (28,660 fontot).
4. Minden Szerződő Államnak, amikor kijelöli azokat a közutakat, amelyekre ezt a függeléket alkalmazni kell, ismertetnie kell az említett utakon a közlekedés számára átmenetileg megengedett méreteket, illetve legnagyobb súlyokat:
a) ha ezeken akár olyan kompok, olyan alagutak, akár pedig olyan hidak vannak, amelyek nem engedik meg a jelen függelékben ismertetett méretű és engedélyezett súlyú járművek áthaladását;
b) ha ez utak jellege és műszaki feltételei elégtelenek ahhoz, hogy az említett áthaladást lehetővé tegyék.
5. Azon járművek vagy kapcsolt járműkombinációk részére, amelyek a fent rögzített méret- vagy maximális súlykorlátozásokat túllépik, minden Szerződő Állam, illetve ez Államok minden alárendelt szerve különleges forgalmi engedélyeket bocsáthat ki.
6. Minden Szerződő Állam vagy az Állam alárendelt szerve egy bizonyos időtartamra korlátozhatja, vagy megtilthatja olyan utakon gépjárművek közlekedését, amelyeket a jelen függelék alkalmazása szempontjából kijelölt, illetőleg megszorításokat alkalmazhat a járművek súlyát illetően azon járművekre nézve, amelyek ilyen úton közlekednek, ha az út megrongálódás, nagy eső, havazás, olvadás, vagy egyéb kedvezőtlen légköri viszonyok miatt a rendes körülmények között megengedett súlyú járművektől súlyos károkat szenvedne.
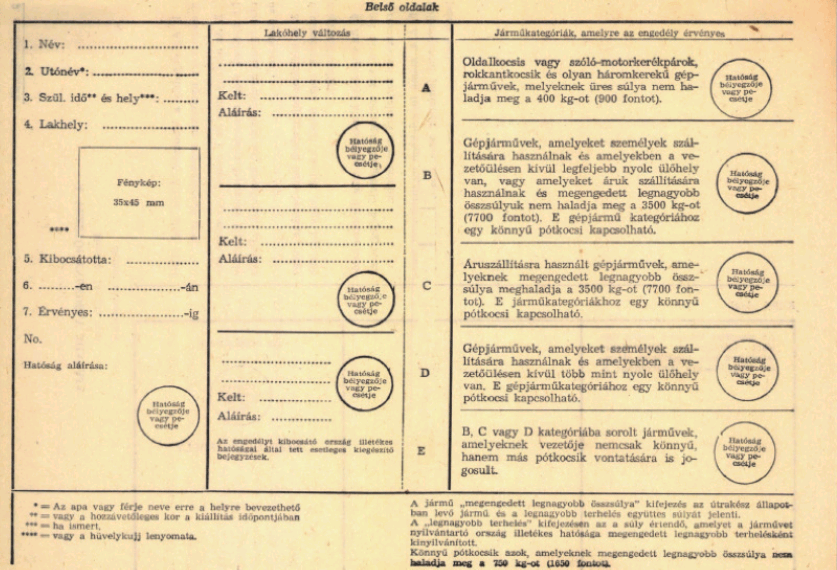
A megengedett legkisebb életkor valamely gépjármű vezetéséhez - az Egyezmény 24. Cikkében előírt feltételeket figyelembe véve - tizennyolc év.
Mégis minden Szerződő Állam vagy alárendelt szerve elismerheti érvényességét azoknak a vezetői engedélyeknek, amelyeket egy másik Szerződő Állam a motorkerékpárok és betegkocsik tizennyolc évnél fiatalabb korú vezetői részére bocsátott ki.
Mérete: 74×105 mm
Színe: rózsaszínű
1. Az engedély a kibocsátó Állam által előírt nyelven vagy nyelveken szövegezendő meg.
2. Az okmány címe, „VEZETŐI ENGEDÉLY”, a fenti 1. pontban előírt nyelven, vagy nyelveken fejezendő ki, amely után francia nyelvű fordítása következik: „Permis de conduire.”
3. A kézírásos bejegyzések latin betűkkel, vagy úgynevezett angol írással írandók (vagy legalább megismétlendők).
4. Az engedélyt kibocsátó ország illetékes hatóságai által tett esetleges kiegészítő bejegyzések a nemzetközi forgalmat nem érintik.
5. A 4. számú függelékben meghatározott megkülönböztető jelzésnek az ovális részben szerepelnie kell.
Külső oldal
| Az engedélyt kibocsátó ország illetékes hatóságainak bejegyzéseire fenntartott hely, ideértve az időszakos megújításokra vonatkozókat is. | Az ország neve Hatóság bélyegzője vagy pecsétje VEZETŐI ENGEDÉLY | ||
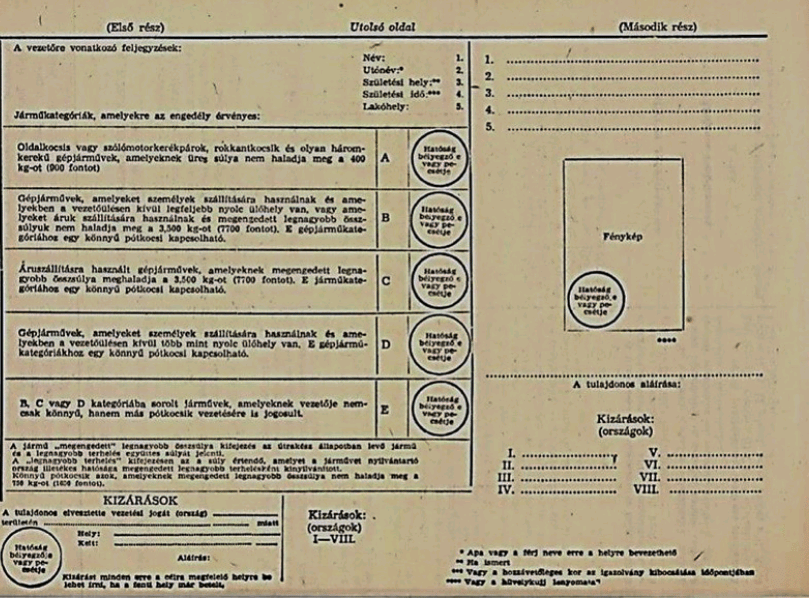
Mérete: 105×148 mm
Színei:
Borítólapja: szürke
Lapjai: fehérek
Az 1. és 2. oldal hazai nyelven, vagy nyelveken szövegezendő meg. Az utolsó oldal teljes egészében franciául szövegezendő.
A pótlapok az utolsó oldal I. részének szövegét ismétlik meg más nyelveken. Ezeket a következő nyelveken kell megszövegezni.
a) Az engedélyt kibocsátó hatóság által előírt nyelven vagy nyelveken;
b) Az Egyesült Nemzetek hivatalos nyelvein;
c) Az engedélyt kibocsátó állam választására bízott legfeljebb hat másik nyelven.
Az engedély különböző nyelvű hivatalos fordítása a Kormányok által közlendő az Egyesült Nemzetek Főtitkárával (mindegyik a rá vonatkozó nyelven).
A kézírásos bejegyzések mindig latin betűkkel írandók vagy úgynevezett angol folyóírással.
1. oldal
(Borítólap)
| (Az ország neve) | |
| Nemzetközi gépjárműforgalom | |
| NEMZETKÖZI VEZETŐI ENGEDÉLY | |
| Az 1949. szeptember 19-i közúti közlekedésre vonatkozó Egyezmény | |
| ................................................................................... | |
| Kibocsátották: ................................................... -ban | |
| .............................................................................. -án | |
| Hatóság bélyegzője vagy pecsétje | |
| A hatóság aláírása vagy bélyegzője vagy a hatóság által felhatalmazott társaság aláírása vagy bélyegzője |
(Fedőlap hátulja)
| A jelen engedély valamennyi szerződő Állam területén érvényes - az engedélyt kiállító Szerződő Állam területét kivéve - a kibocsátás napjától számított egy éven belül az utolsó oldalon megjelölt kategóriába, vagy kategóriákba tartozó járművek vezetésére. | |
| (A Szerződő Államok tetszés szerinti felsorolására fenntartott hely) | |
| Magától értetődően a jelen engedély semmi szín alatt nem menti fel tulajdonosát az alól a kötelezettség alól, hogy abban az államban, ahol éppen van, vagy közlekedik, teljes mértékben alkalmazkodjék azokhoz az érvényes törvényekhez és szabályokhoz, amelyek valamely foglalkozás megkezdésére vagy gyakorlására vonatkoznak. | |
A Magyar Népköztársaság az Egyezményhez az alábbi fenntartással csatlakozott:
A Magyar Népköztársaság az Egyezmény 33. Cikkének rendelkezéseit magára nézve nem tekinti kötelezőnek.
(Geneva, 19 September 1949)
The Contracting States, desirous of promoting the development and safety of international road traffic by establishing certain uniform rules, have agreed upon the following provisions:
1. While reserving its jurisdiction over the use of its own roads, each Contracting State agrees to the use of its roads for international traffic under the conditions set out in this Convention.
2. No Contracting State shall be required to extend the benefit of the provisions of this Convention to any motor vehicle or trailer, or to any driver having remained within its territory for a continuous period exceeding one year.
1. The Annexes to this Convention shall be considered as integral parts of the Convention; it being understood, however, that any State may on signature or ratification of, or accession to, the Convention, or at any time thereafter, by declaration exclude Annexes 1 and 2 from its application of the Convention.
2. Any Contracting State may at any time give notice to the Secretary-General of the United Nations that it will be bound, as from the date of the said notification, by Annexes 1 and 2 as excluded under the terms of paragraph 1 of this Article.
1. Measures which all the Contracting States or certain of them may have agreed, or shall in the future agree, to put into effect with a view to facilitating international road traffic by simplifying customs, police, health or other requirements will be regarded as being in conformity with the object of this Convention.
2. (a) A bond or other form of security guaranteeing payment of any import duties and import taxes which would, in the absence of such security, be chargeable on the importation of any motor vehicle admitted to international traffic may be required by any Contracting State;
(b) A Contracting State shall accept for the purposes of this Article the guarantee of an organization established in its own territory affiliated to an international association which has issued a valid international customs pass for the motor vehicle (such as a carnet de passages en douane).
3. For the fulfilment of the requirements provided for in this Convention the Contracting States will endeavour to keep open during the same hours customs offices and posts next to each other on the same international road.
1. For the purpose of this Convention the following expressions shall have the meanings hereby assigned to them:
„International traffic” means any traffic which crosses at least one frontier;
„Road” means any way open to the public for the circulation of vehicles;
„Carriageway” means that portion of a road normally used by vehicular traffic;
„Lane” means any one of the parts into which the carriageway is divisible, each sufficient in width for one moving line of vehicles;
„Driver” means any person who drives a vehicle, including cycles, or guides draught, pack or saddle animals or herds or flocks on a road, or who is in actual physical control of the same;
„Motor vehicle” means any self-propelled vehicle normally used for the transport of persons or goods upon a road, other than vehicles running on rails or connected to electric conductors. Any State bound by Annex 1 shall exclude from this definition cycles fitted with an auxiliary engine of the type described in that Annex;
„Articulated vehicle” means any motor vehicle with a trailer having no front axle and so attached that part of the trailer is superimposed upon the motor vehicle and a substantial part of the weight of the trailer and of its load is borne by the motor vehicle. Such a trailer shall be called a „semi-trailer”;
„Trailer” means any vehicle designed to be drawn by a motor vehicle;
„Cycle” means any cycle not self-propelled. Any State bound by Annex 1 shall include in this definition cycles fitted with an auxiliary engine of the type described in that Annex;
„Laden weight” of a vehicle means the weight of the vehicle and its load when the vehicle is stationary and ready for the road, and shall include the weight of the driver and of any other persons carried for the time being;
„Maximum load” means the weight of the load declared permissible by the competent authority of the country of registration of the vehicle; „Permissible maximum weight” of a vehicle means the weight of the vehicle and its maximum load when the vehicle is ready for the road.
„Permissible maximum weight” of a vehicle means the weight of the vehicle and its maximum load when the vehicle is ready for the road.
This Convention is not to be taken as authorizing the carriage of persons for hire or reward or the carriage of goods other than the personal baggage of the occupants of the vehicle; it being understood that these matters and all other matters not provided for in this Convention remain within the competence of domestic legislation, subject to the application of other relevant international conventions or agreements.
Each Contracting State shall take appropriate measures to ensure the observance of the rules set out in this Chapter.
Every driver, pedestrian or other road user shall conduct himself in such a way as not to endanger or obstruct traffic; he shall avoid all behaviour that might cause damage to persons, or public or private property.
1. Every vehicle or combination of vehicles proceeding as a unit shall have a driver.
2. Draught, pack or saddle animals shall have a driver, and cattle shall be accompanied, except in special areas which shall be marked at the points of entry.
3. Convoys of vehicles and animals shall have the number of drivers prescribed by domestic regulations.
4. Convoys shall, if necessary, be divided into sections of moderate length, and be sufficiently spaced out for the convenience of traffic. This provision does not apply to regions where migration of nomads occurs.
5. Drivers shall at all times be able to control their vehicles or guide their animals. When approaching other road users, they shall take such precautions as may be required for the safety of the latter.
1. All vehicular traffic proceeding in the same direction on any road shall keep to the same side of the road, which shall be uniform in each country for all roads. Domestic regulations concerning one-way traffic shall not be affected.
2. As a general rule and whenever the provisions of Article 7 so require, every driver shall:
(a) on two-lane carriageways intended for two-way traffic, keep his vehicle in the lane appropriate to the direction in which he is travelling;
(b) on carriageways with more than two lanes, keep his vehicle in the lane nearest to the edge of the carriageway appropriate to the direction in which he is travelling.
3. Animals shall be kept as near as possible to the edge of the road in accordance with domestic regulations.
The driver of a vehicle shall at all times have its speed under control and shall drive in a reasonable and prudent manner. He shall slow down or stop whenever circumstances so require, and particularly when visibility is not good.
1. Drivers when meeting or being overtaken shall keep as close as practicable to the edge of the carriageway on the side appropriate to the direction in which they are travelling. In overtaking, a driver shall pass on the left or the right of the overtaken vehicle or animal according to the rule observed in the country concerned. These rules shall not necessarily apply in the case of tramcars, trains on roads, and certain mountain roads.
2. On the approach of any vehicle or accompanied animal, drivers shall:
(a) when meeting, leave sufficient space for the vehicle or accompanied animal coming from the opposite direction;
(b) when being overtaken, keep as close as practicable to the appropriate edge of the carriageway and not accelerate.
3. Drivers intending to overtake shall make sure that there is sufficient room and sufficient visibility ahead to permit overtaking without danger. After overtaking they shall bring their vehicles back to the right or left hand side according to the rule observed in the country concerned, but only after making sure that this will not inconvenience the vehicle, pedestrian or animal overtaken.
1. Every driver approaching a fork, crossroads, road junction or level-crossing shall take special precautions to avoid accidents.
2. Priority of passage may be accorded at intersections on certain roads or sections of road. Such priority shall be marked by signs and every driver approaching such a road or section of road shall be bound to yield the right of way to drivers travelling along it.
3. The provisions of Annex 2 regarding the priority of passage at intersections not covered by paragraph 2 of this Article shall be applied by the States bound by the said Annex.
4. Every driver before starting to turn into a road shall:
(a) Make sure that he can do so without danger to other road users;
(b) Give adequate notice of his intention to turn;
(c) Move over as far as practicable to the edge of the carriageway on the side appropriate to the direction in which he is travelling if he wishes to turn off the road on that side;
(d) Move as near as practicable towards the middle of the carriageway if he wishes to leave the road and turn to the other side, except as provided for in paragraph 2 of Article 16;
(e) In no case hamper the traffic coming from the opposite direction.
1. Stationary vehicles or animals shall be kept off the carriageway if feasible, or, if not, as close as practicable to the edge of the carriageway. Drivers shall not leave vehicles or animals until they have taken all necessary precautions to avoid an accident.
2. Vehicles and animals shall not be left waiting where they are likely to cause danger or obstruction, and in particular at or near a road intersection, a bend or the top of a hill.
All necessary precautions shall be taken to ensure that the load of a vehicle shall not be a cause of damage or danger.
1. From nightfall and during the night, or when atmospheric conditions render it necessary, every vehicle or combination of vehicles on a road shall show at least one white light in front and at least one red light in the rear.
When a vehicle, other than a cycle or a motorcycle without sidecar, is provided with only one white light in front, this shall be placed on the side nearest to traffic coming from the opposite direction.
In countries where two white front lights are obligatory, such lights shall be placed one on the right and one on the left of the vehicle.
The red light may be produced either by a device distinct from that which produces the white light or lights in front or by the same device when the vehicle is short enough and so arranged as to permit this.
2. In no case shall a vehicle have a red light or a red reflector directed to the front or a white light or a white reflector directed to the rear. This provision shall not apply to a white or yellow reversing light in cases where the domestic legislation of the country of registration of the vehicle permits such lights.
3. Lights and reflex reflectors shall be such as to ensure that the vehicle is clearly indicated to other road users.
4. Any Contracting State or subdivision thereof may, provided that all measures are taken to guarantee normal conditions of safety, exempt from certain provisions of this Article.
(a) Vehicles used for special purposes or under special conditions;
(b) Vehicles of special shape and kind;
(c) Stationary vehicles on adequately lighted roads.
1. The provisions of this Chapter shall apply to trolley-buses.
2. (a) Cyclists shall use cycle tracks where there is an obligation to do so indicated by an appropriate sign, or where such obligation is imposed by domestic regulations;
(b) Cyclists shall proceed in single file where circumstances so require and, except in special cases provided for in domestic regulations, shall never proceed more than two abreast on the carriageway;
(c) Cyclists shall not be towed by vehicles;
(d) The provisions of paragraph 4(d) of Article 12 shall not apply to cyclists where domestic regulations provide
1. With a view to ensuring a homogeneous system, the road signs and signals adopted in each Contracting State shall, as far as possible, be the only ones to be placed on the roads of that State. Should it be necessary to introduce any new sign, the shape, colour and type of symbol employed shall conform with the system in use in that State.
2. The number of approved signs shall be limited to such as may be strictly necessary. They shall be placed only at points where they are essential.
3. The danger signs shall be placed at a sufficient distance from the object indicated to give road users adequate warning.
4. The affixing to an approved sign of any notice not related to the purpose of such sign and liable to obscure it or to interfere with its character shall be prohibited.
5. All boards and notices which might be confused with the approved signs or make them more difficult to read shall be prohibited.
1. In order to be entitled to the benefits of this Convention, a motor vehicle shall be registered by a Contracting State or subdivision thereof in the manner prescribed by its legislation.
2. A registration certificate containing at least the serial number, known as the registration number, the name or the trade mark of the maker of the vehicle, the maker’s identification or serial number, the date of first registration and the full name and permanent place of residence of the applicant for the said certificate shall be issued either by the competent authority or by an association duly empowered to do so.
3. This certificate shall be accepted by all Contracting States as prima facie evidence of the information entered thereon.
1. Every motor vehicle shall display at least at the back on a special plate or on the vehicle itself, a registration number issued or allotted by the competent authority. In the case of a motor vehicle drawing one or more trailers the single trailer or the last trailer shall display the registration number of the drawing vehicle or its own registered number.
2. The composition of the registration number and the manner in which it is displayed shall be as set out in Annex 3.
1. Every motor vehicle shall in addition to the registration number display at the back, inscribed on a plate or on the vehicle itself, the distinguishing sign of the place of registration of this vehicle. This sign shall indicate either a State or a territory which constitutes a distinct unit from the point of view of registration. In the case of a motor vehicle drawing one or more trailers this sign shall also be displayed at the back of the single trailer or of the last trailer.
2. The composition of the distinguishing sign and the manner in which it is displayed shall be as set out in Annex 4.
Every motor vehicle and trailer shall carry the identification marks set out in Annex 5.
1. Every motor vehicle and trailer shall be in good working order and in such safe mechanical condition as not to endanger the driver, other occupants of the vehicle or any person upon the road, or cause damage to public or private property.
2. In addition, every motor vehicle, or trailer, and its equipment shall conform to the provisions of Annex 6 and the driver of every motor vehicle shall observe the rules set out therein.
3. The provisions of this Article shall apply to trolley-buses.
1. The maximum dimensions and weights of vehicles permitted to travel on the roads of each Contracting State or subdivision thereof shall be matters for domestic legislation. On certain roads designated by States Parties to regional agreements or, in the absence of such agreements, by a Contracting State, the permissible maximum dimensions and weights shall be those set out in Annex 7.
2. The provisions of this Article shall apply to trolleybuses.
1. Each Contracting State shall allow any driver admitted to its territory who fulfils the conditions which are set out in Annex 8 and who holds a valid driving permit issued to him, after he has given proof of his competence, by the competent authority of another Contracting State or subdivision thereof, or by an Association duly empowered by such authority, to drive on its roads without further examination motor vehicles of the category or categories defined in Annexes 9 and 10 for which the permit has been issued.
2. A Contracting State may however require that any driver admitted to its territory shall carry an international driving permit conforming to the model contained in Annex 10, especially in the case of a driver coming from a country where a domestic driving permit is not required or where the domestic permit issued to him does not conform to the model contained in Annex 9.
3. The international driving permit shall, after the driver has given proof of his competence, be delivered by the competent authority of a Contracting State or subdivision thereof, or by a duly authorised Association, and sealed or stamped by such authority or Association. The holder shall be entitled to drive in all Contracting States without further examination motor vehicles coming within the categories for which the permit has been issued.
4. The right to use the domestic as well as the international driving permit may be refused if it is evident that the conditions of issue are no longer fulfilled.
5. A Contracting State or a subdivision thereof may withdraw from the driver the right to use either of the abovementioned permits only if the driver has committed a driving offence of such a nature as would entail the forfeiture of his driving permit under the legislation and regulations of that Contracting State. In such an event, the Contracting State or subdivision thereof withdrawing the use of the permit may withdraw and retain the permit until the period of the withdrawal of use expires or until the holder leaves the territory of that Contracting State, whichever is the earlier, and may record such withdrawal of use on the permit and communicate the name and address of the driver to the authority which issued the permit.
6. During a period of five years beginning with the entry into force of this Convention, any driver admitted to international traffic under the provisions of the International Convention relative to Motor Traffic signed at Paris on 24 April 1926, or of the Convention on the Regulation of Inter-American Automotive Traffic opened for signature at Washington on 15 December 1943, and holding the documents required thereunder, shall be considered as fulfilling the requirements of this Article.
The Contracting States undertake to communicate to each other such information as will enable them to establish the identity of persons holding domestic or international driving permits when they are liable to proceedings for a driving offence. They further undertake to make known the information required to establish the identity of the owner or the person in whose name a foreign vehicle which has been involved in a serious accident is registered.
Every cycle shall be equipped with:
(a) at least one efficient brake;
(b) an audible warning device consisting of a bell, to the exclusion of any other audible warning device, capable of being heard at a reasonable distance;
(c) a white or yellow light in front and a red light or a red reflex reflector in the rear from nightfall and during the night or when atmospheric conditions render it necessary.
1. This Convention shall be open, until 31 December 1949, for signature by all States Members of the United Nations and by every State invited to attend the United Nations Conference on Road and Motor Transport held at Geneva in 1949.
2. This Convention shall be ratified and the instruments of ratification deposited with the Secretary-General of the United Nations.
3. From 1 January 1950, this Convention shall be open for accession by those of the States referred to in paragraph 1 of this Article which have not signed this Convention and by any other State which the Economic and Social Council may by resolution declare to be eligible. It shall also be open for accession on behalf of any Trust Territory of which the United Nations is the administering authority.
4. Accession shall be effected by the deposit of an instrument of accession with the Secretary-General of the United Nations.
1. Any State may, at the time of signature, ratification or accession, or at any time thereafter, declare, by notification addressed to the Secretary-General of the United Nations, that the provisions of this Convention will be applicable to all or any of the territories for the international relations of which it is responsible. These provisions shall become applicable in the territories named in the notification thirty days after the date of receipt of such notification by the Secretary-General or, if the Convention has not entered into force at that time, then upon the date of its entry into force.
2. Each Contracting State, when circumstances permit, undertakes to take as soon as possible the necessary steps in order to extend the application of this Convention to the territories for the international relations of which it is responsible, subject, where necessary for constitutional reasons, to the consent of the governments of such territories.
3. Any State which has made a declaration under paragraph 1 of this Article applying this Convention to any territory for the international relations of which it is responsible may at any time thereafter declare by notification given to the Secretary-General that the Convention shall cease to apply to any territory named in the notification and the Convention shall, after the expiration of one year from the date of the notification, cease to apply to such territory.
This Convention shall enter into force on the thirtieth day after the date of the deposit of the fifth instrument of ratification or accession. This Convention shall enter into force for each State ratifying or acceding after that date on the thirtieth day after the deposit of its instrument of ratification or accession. The Secretary-General of the United Nations shall notify each of the signatory or acceding States and every other state invited to attend the United Nations Conference on Road and Motor Transport of the date on which this Convention enters into force.
This Convention shall terminate and replace, in relations between the Contracting States, the International Convention relative to Motor Traffic and the International Convention relative to Road Traffic signed at Paris on 24 April 1926, and the Convention on the Regulation of Inter-American Automotive Traffic opened for signature at Washington on 15 December 1943.
1. Any amendment to this Convention may be proposed by any Contracting State. The text of such proposed amendment shall be communicated to the Secretary-General of the United Nations who shall transmit it to each Contracting State with a request that such State reply within four months stating whether it:
(a) Desires that a conference be convened to consider the proposed amendment; or
(b) Favours the acceptance of the proposed amendment without a conference; or
(c) Favours the rejection of the proposed amendment without a conference.
The proposed amendment shall also be transmitted by the Secretary-General to all States, other than Contracting States, invited to attend the United Nations Conference on Road and Motor Transport.
2. The Secretary-General shall convene a conference of the Contracting States to consider the proposed amendment, if the convening of a conference is requested:
(a) by at least one-quarter of the Contracting States in the case of a proposed amendment to any part of the Convention other than the Annexes;
(b) by at least one-third of the Contracting States in the case of a proposed amendment to an Annex other than Annexes 1 and 2;
(c) in the case of Annexes 1 and 2 by at least one-third of the States bound by the Annex to which an amendment has been proposed. The Secretary-General shall invite to the Conference such States, other than Contracting States, invited to attend the United Nations Conference on Road and Motor Transport or whose participation would, in the opinion of the Economic and Social Council, be desirable. The provisions of this paragraph shall not apply in cases where an amendment to the Convention has been adopted in accordance with paragraph 5 of this Article.
3. Any amendment to this Convention which shall be adopted by a two-thirds majority vote of a conference shall be communicated to all Contracting States for acceptance. Ninety days after its acceptance by two-thirds of the Contracting States each amendment to the Convention, except for those to Annexes 1 and 2, shall enter into force for all the Contracting States except those which, before it enters into force, make a declaration that they do not adopt the amendment. For the entry into force of any amendment to Annexes 1 and 2 the majority shall be two-thirds of the States bound by the amended Annex.
4. The Conference may by a two-thirds majority vote determine at the time of the adoption of an amendment to this Convention, except for those to Annexes 1 and 2, that the amendment is of such a nature that any Contracting State which has made a declaration that it does not accept the amendment and which then does not accept the amendment within a period of twelve months after the amendment enters into force shall, upon the expiration of this period, cease to be a party to the Convention.
5. In the event of a two-thirds majority of the Contracting States informing the Secretary-General pursuant to paragraph 1(b) of this Article that they favour the acceptance of the amendment without a conference, notification of their decision shall be communicated by the Secretary-General to all the Contracting States. The amendment shall upon the expiration of ninety days from the date of such notification become effective as regards all the Contracting States except those States which notify the Secretary-General that they object to such an amendment within that period.
6. As regards amendments to Annexes 1 and 2, and any amendment not within the scope of paragraph 4 of this Article, the existing provisions shall remain in force in respect of any Contracting State which has made a declaration or lodged an objection with respect to such an amendment.
7. A Contracting State which has made a declaration in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 3 of this Article, or has lodged an objection in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 5 of this Article to an amendment, may withdraw such declaration or objection at any time by notification addressed to the Secretary-General. The amendment shall be effective as regards that State upon receipt of such notification by the Secretary-General.
This Convention may be denounced by means of one year’s notice given to the Secretary-General of the United Nations, who shall notify each signatory or acceding State thereof. After the expiration of this period the Convention shall cease to be in force as regards the Contracting State which denounces it.
Any dispute between any two or more Contracting States concerning the interpretation or application of this Convention, which the Parties are unable to settle by negotiation or by another mode of settlement, may be referred by written application from any of the Contracting States concerned to the International Court of Justice for decision.
Nothing in this Convention shall be deemed to prevent a Contracting State from taking action compatible with the provisions of the Charter of the United Nations and limited to the exigencies of the situation which it considers necessary for its external or internal security.
1. The Secretary-General shall, in addition to the notifications provided for in Article 29, paragraphs 1, 3 and 5 of Article 31 and Article 32, notify the States referred to in paragraph 1 of Article 27 of the following:
(a) Declarations by Contracting, States that they exclude Annex 1, Annex 2, or both of them, from the application of the Convention in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 2;
(b) Declarations by Contracting States that they shall be bound by Annex 1, Annex 2, or both of them, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 2;
(c) Signatures, ratifications and accessions in accordance with Article 27;
(d) Notifications with regard to the territorial application of the Convention in accordance with Article 28;
(e) Declarations whereby States accept amendments to the Convention in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 31;
(f) Objections to amendments to the Convention communicated by States to the Secretary-General in accordance with paragraph 5 of Article 31;
(g) The date of entry into force of amendments to the Convention in accordance with paragraphs 3 and 5 of Article 31;
(h) The date on which a State has ceased to be a Party to the Convention, in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 31;
(i) Withdrawals of objections to an amendment in accordance with paragraph 7 of Article 31;
(j) The list of States bound by any amendment to the Convention;
(k) Denunciations of the Convention in accordance with Article 32;
(l) Declarations that the Convention has ceased to apply to a territory in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 28;
(m) Notifications with respect to distinctive letters made by States in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 3 of Annex 4.
2. The original of this Convention shall be deposited with the Secretary-General who will transmit certified copies thereof to the States referred to in paragraph 1 of Article 27.
3. The Secretary-General is authorized to register this Convention upon its entry into force.
IN WITNESS WHEREOF the undersigned representatives, after having communicated their full powers, found to be in good and due form, have signed this Convention.
DONE at Geneva, in a single copy, in the English and French languages, both texts authentic, this nineteenth day of September, one thousand nine hundred and forty-nine.
(Signatures)
Cycles fitted with an auxiliary internal combustion engine having a maximum cylinder capacity of 50 cm3 (3.05 cu. in.) shall not be considered as motor vehicles, provided that they retain all the normal characteristics of cycles with respect to their structure.
1. When any two vehicles are simultaneously approaching a road intersection by roads of which one does not enjoy priority over the other, the vehicle approaching from the left in countries where the direction of traffic is on the right, and from the right in countries where the direction of traffic is on the left, shall yield the right of way to the other vehicle.
2. The right of priority shall not necessarily apply in the case of tramcars and trains on roads.
1. The registration number of a vehicle shall consist either of figures or of figures and letters. The figures shall be in Arabic numerals as used in United Nations documents and the letters in Latin characters. When other numerals or characters are used, they shall be repeated in the numerals or characters of the types mentioned above.
2. The number shall be legible in normal daylight at a distance of 20 m. (65 feet).
3. When the registration number is displayed on a special plate, this plate shall be fixed in a vertical or nearly vertical position and in a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle itself. When the number is fixed to or painted on the vehicle itself, this shall be done on a vertical or nearly vertical surface at the back of the vehicle.
4. The rear registration number shall be illuminated as prescribed in Annex 6.
1. The distinguishing sign shall be composed of one to three letters in capital Latin characters. The letters shall have a minimum height of 80 mm. (3.1 in.) and their strokes a width of 10 mm. (0.4 in.). The letters shall be painted in black on a white ground of elliptical form with the major axis horizontal.
2. If the distinguishing sign is composed of three letters, the dimensions of the ellipse shall be at least 240 mm. (9.4 in.) in width and 145 mm. (5.7 in.) in height. The dimensions may be reduced to 175 mm. (6.9 in.) in width and 115 mm. (4.5 in.) in height if the sign carries less than three letters.
3. As regards the distinguishing signs for motorcycles, the dimensions of the ellipse, whether the sign is composed of one, two or three letters, may be reduced to 175 mm. (6.9 in.) in width and 115 mm. (4.5 in.) in height. 3. The distinctive letters for the different States and territories are as follows:
Andorra .................................................................................... AND
Algeria ...................................................................................... DZ
Argentina .................................................................................. RA
Australia .................................................................................... AUS
Austria ....................................................................................... A
Barbados ................................................................................... BDS
Belgium ..................................................................................... B
Botswana ................................................................................... RB
Brazil ......................................................................................... BR
Bulgaria ..................................................................................... BG
Burma ........................................................................................ BUR
Cambodia ................................................................................... K
Canada ....................................................................................... CDN
Central African Republic ........................................................... RCA
Ceylon ........................................................................................ CL
Chile ........................................................................................... RCH
China .......................................................................................... RC
Congo (Brazzaville) ................................................................... RCB
Congo (Dem. Rep. of) ............................................................... CGO
Costa Rica ................................................................................. CR
Cyprus ........................................................................................ CY
Czechoslovakia .......................................................................... CS
Dahomey .................................................................................... DY
Denmark .................................................................................... DK
Dominican Republic .................................................................. DOM
Ecuador ..................................................................................... EC
Finland ....................................................................................... SF
France ........................................................................................ F
French Overseas Territories ...................................................... F
Gambia ...................................................................................... WAG
Ghana ........................................................................................ GH
Greece ....................................................................................... GR
Guatemala ................................................................................. GCA
Haiti .......................................................................................... RH
Holy See .................................................................................... V
Hungary .................................................................................... H
Iceland ...................................................................................... IS
India ......................................................................................... IND
Indonesia .................................................................................. RI
Iran ........................................................................................... IR
Ireland ...................................................................................... IRL
Israel ......................................................................................... IL
Italy ........................................................................................... I
Ivory Cost ................................................................................. CI
Jamaica ..................................................................................... JA
Japan ......................................................................................... J
Jordan ....................................................................................... HKJ
Kenya ....................................................................................... EAK
Laos .......................................................................................... LAO
Lebanon .................................................................................... RL
Lesotho ..................................................................................... LS
Luxembourg ............................................................................. L
Madagascar .............................................................................. RM
Malawi ..................................................................................... MW
Malaysia ................................................................................... PTM
Mali .......................................................................................... RMM
Malta ........................................................................................ M
Mexico ..................................................................................... MEX
Monaco .................................................................................... MC
Morocco ................................................................................... MA
Netherlands .............................................................................. NL
Surinam ............................................................................. SME
Netherlands Antilles .......................................................... NA
New Zealand ........................................................................... NZ
Nicaragua ................................................................................ NIC
Niger ....................................................................................... NIG
Nigeria .................................................................................... WAN
Norway ................................................................................... N
Pakistan .................................................................................. PAK
Paraguay ................................................................................ PY
Peru ........................................................................................ PE
Philippines .............................................................................. PI
Poland ..................................................................................... PL
Portugal ................................................................................... P
Romania .................................................................................. R
Rwanda ................................................................................... RWA
San Marino .............................................................................. RSM
Senegal .................................................................................... SN
Sierra Leone ............................................................................. WAL
Singapore ................................................................................. SGP
South Africa ............................................................................. ZA
Spain ........................................................................................ E
African localities and provinces .............................................. E
Sweden .................................................................................... S
Switzerland .............................................................................. CH
Syria ......................................................................................... SYR
Thailand ................................................................................... T
Togo ......................................................................................... TG
Trinidad and Tobago ................................................................ TT
Tunisia ...................................................................................... TN
Turkey ....................................................................................... TR
Uganda ..................................................................................... EAU
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ........................................ SU
United Arab Republic .............................................................. ET
United Kingdom ...................................................................... GB
Aden ................................................................................. AND
Alderney ............................................................................ GBA
Bahamas ............................................................................ BS
British Honduras ................................................................ BH
Brunei ................................................................................. BRU
Guernsey ............................................................................ GBG
Gibraltar ............................................................................. GBZ
Jersey ................................................................................. GBJ
Hong Kong ......................................................................... HK
Mauritius ............................................................................ MS
Province Wellesley ............................................................. SS
Seychelles ........................................................................... SY
Southern Rhodesia .............................................................. SR
Swaziland ........................................................................... SD
Windward Islands
Grenada ............................................................................. WG
St. Lucia ............................................................................. WL
St. Vincent ......................................................................... WV
United Republic of Tanzania
Tanganyika ............................................................................... EAT
Zanzibar .................................................................................... EAZ
United States of America .......................................................... USA
Uruguay .................................................................................... U
Venezuela ................................................................................. YV
Viet-Nam (Republic of) ............................................................ VN
Western Samoa ......................................................................... WS
Yugoslavia ................................................................................ YU
Zambia ...................................................................................... RNR
Any State which has not already done so shall on signature or ratification of, or accession to, this Convention, notify the Secretary-General of the distinctive letters selected by that State.
4. When the distinguishing sign is carried on a special plate this plate shall be fixed in a vertical or nearly vertical position and in a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle itself. When the sign is fixed to or painted on the vehicle itself, this shall be done on a vertical or nearly vertical surface at the back of the vehicle.
1. The identification marks shall comprise:
(a) In the case of a motor vehicle:
(i) The name or the trade mark of the maker of the vehicle,
(ii) On the chassis or, in the absence of a chassis, on the body, the maker’s identification or serial number,
(iii) On the engine, the maker’s engine number if such a number is placed thereon by the maker,
(b) In the case of a trailer, either the information referred to in (i) and (ii) above or an identification mark issued for the trailer by the competent authority.
2. The marks mentioned above shall be placed in accessible positions and shall be in a form easily legible and not capable of being easily removed or altered.
I. BRAKING
(a) Braking of motor vehicles other than motor cycles with or without sidecars
Every motor vehicle shall be equipped with brakes capable of controlling the movement of and of stopping the vehicle in an efficient, safe and rapid way under any conditions of loading on any up or down gradient on which the vehicle is operated.
The braking shall be operated by means of two devices so constructed that, in the event of failure of one of the braking devices, the other shall be capable of stopping the vehicle within a reasonable distance.
For the purpose of this Annex, one of these braking devices will be called the „service brake” and the other one the „parking brake”.
The parking brake shall be capable of being secured, even in the absence of the driver, by direct mechanical action.
Either means of operation shall be capable of applying braking force to wheels symmetrically placed on each side of the longitudinal axis of the vehicle.
The braking surfaces shall always be connected with the wheels of the vehicle in such a way that it is not possible to disconnect them otherwise than momentarily by means of a clutch, gear box or free wheel.
One at least of the braking devices shall be capable of acting on braking surfaces directly attached to the wheels of the vehicle or attached through parts not liable to failure.
(b) Braking of trailers
Every trailer having a permissible maximum weight exceeding 750 kg. (1,650 lbs.) shall be equipped with at least one braking device acting on wheels placed symmetrically on each side of the longitudinal axis of the vehicle and acting on at least half the number of wheels.
The provisions of the preceding paragraph shall be required, however, in respect of trailers if the permissible maximum weight does not exceed 750 kg. (1,650 lbs.) but exceeds one-half of the unladen weight of the drawing vehicle.
The braking device of trailers with a permissible maximum weight exceeding 3,500 kg. (7,700 lbs.) shall be capable of being operated by applying the service brake from the drawing vehicle. When the permissible maximum weight of the trailer does not exceed 3,500 kg. (7,700 lbs.) its braking device may be brought into action merely by the trailer moving upon the drawing vehicle (overrun braking).
The braking device of the trailer shall be capable of preventing the rotation of the wheels when the trailer is uncoupled.
Any trailer equipped with a brake shall be fitted with a device capable of automatically stopping the trailer if it becomes detached whilst in motion. This provision shall not apply to two-wheeled camping trailers or light luggage trailers whose weight exceeds 750 kg. (1,650 lbs.) provided that they are equipped in addition to the main attachment with a secondary attachment which may be a chain or a wire rope.
(c) Braking of articulated vehicles and combinations of motor vehicles and trailers
(i) Articulated vehicles The provisions of paragraph (a) of this Part shall apply to every articulated vehicle. A semi-trailer having a permissible maximum weight exceeding 750 kg. (1,650 lbs.) shall be equipped with at least one braking device capable of being operated by applying the service brake from the drawing vehicle.